Many website owners at first would usually pay or rent for shared web hosting services to host their websites and applications. But as their businesses expand with a corresponding growth of web traffic to their sites, there will be more demand for online functions and resources that shared web hosting service providers may not be able to provide.
That’s why virtual private server (VPS) hosting can be a good choice for website owners like you who need a more reliable, powerful and secure web hosting option that can keep up with the growth of traffic to your website and its related applications and services.
If you are new to VPS servers and VPS hosting, this guide will be a great help for you in learning about the commonly asked questions about VPS such as what is a VPS server, how do VPS servers work, what is a VPS hosting service and how much for VPS hosting. You will also learn about other interesting subjects that are related to VPS servers and hosting.
What is a VPS Server
 A VPS is a virtual machine that is a software-based replica or simulation of a physical server. Every VPS is installed in a physical server that is operated by a web server hosting company or VPS service provider that operates multiple VPS machines in its data center facility. The provider uses virtualization technology to split a single physical server into multiple private virtual or simulated server environments. In layman’s terms, a single VPS machine contains several separate virtual servers with each of them having its own resources and each simulated server allocated to a single client or user.
A VPS is a virtual machine that is a software-based replica or simulation of a physical server. Every VPS is installed in a physical server that is operated by a web server hosting company or VPS service provider that operates multiple VPS machines in its data center facility. The provider uses virtualization technology to split a single physical server into multiple private virtual or simulated server environments. In layman’s terms, a single VPS machine contains several separate virtual servers with each of them having its own resources and each simulated server allocated to a single client or user.
How do VPS Servers Work
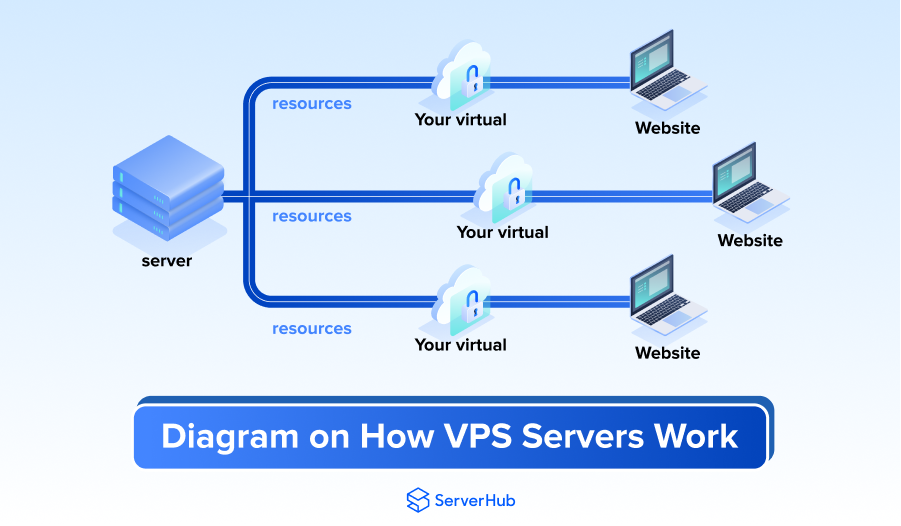 A VPS hosting service provider uses a software known as hypervisor to enable virtualization in a VPS machine. The hypervisor implements a virtual layer on top of the operating system (OS) in the machine to partition or split it into several virtual environments or compartments. In the physical server, the provider installs a virtual layer on top of the OS functioning on the server. The layer then divides the physical machine into partitions of virtual servers with each partition having space for the installation of OS, software and other resources.
A VPS hosting service provider uses a software known as hypervisor to enable virtualization in a VPS machine. The hypervisor implements a virtual layer on top of the operating system (OS) in the machine to partition or split it into several virtual environments or compartments. In the physical server, the provider installs a virtual layer on top of the OS functioning on the server. The layer then divides the physical machine into partitions of virtual servers with each partition having space for the installation of OS, software and other resources.
The partitions between the virtual servers will allow you to install your own OS, websites, applications and other specialized services into the specific virtual server allocated for you. This means your server is private and separated from the other servers on the OS level, and your services are hosted in a secured environment with guaranteed allocation for disk space, bandwidth, memory, CPU cores and other necessary resources to run your website and apps.
Each virtual environment in a VPS machine also has its own user with the necessary resources allocated for each of them and functioning independently from one another. Even though you are still sharing the same physical server with other users, you pay a specific amount for the resources that are guaranteed for your VPS and your server cannot be used by other users who are hosted in the same physical machine.
How Much Traffic Can a VPS Server Handle
An increase in web traffic is one of the major reasons why website owners would transfer the hosting of their websites from shared hosting to VPS hosting service. But do you really know how much traffic or number of visitors that a VPS machine can accommodate? On the average, a VPS can manage more than 10,000 daily visitors, but it can also manage as high as 50,000 daily visitors. However, websites that are heavy on dynamic content like having lots of graphics and multimedia, the VPS will usually handle from 10,000 to 20,000 daily visitors only.
The specific number of daily visitors that a VPS can handle will really depend on your specific VPS hosting plan and the bandwidth consumed by your website. Before choosing a VPS hosting plan, ask the VPS service provider about the features such as CPU, disk space, memory, bandwidth and how these resources can handle the amount of web traffic to your website.
A VPS machine’s actual capacity for handling website visitors will also depend on these specific factors:
- How well optimized is the website’s design and content.
- Types of server requests received by the site.
- Resources allocated to the VPS.
- Number of current visitors especially during peak hours and off-peak hour.
- The time needed for the server to process a request.
Tips on How to Back Up a VPS Server
Data loss due to accidental deletion, hacking, ransomware and other security threats is a serious issue that affects many website owners. That’s why it’s important for you to regularly back up your VPS server because it will help:
- Restore a file or folder that was corrupted or deleted due to human errors, system malfunctions or security attacks.
- Recover the entire server to a previous restore point after a massive data loss.
- Protect and secure your data so your website and apps can continue to function with little or no disturbance to your operations.
The important tips for backing up your VPS server:
1. Decide on a backup location
The first things to consider are which data you want to backup and where to back it up. Selecting the specific backup destinations for different data types will make data recovery much faster when an incident happens. The backup locations for your VPS service can include Bash scripts, cPanel, MySQL Database backups, remote cloud servers, and WebHost Manager. Off-site backup locations are good options, but data recovery can take longer if only a single file needs to be restored and not the whole server.
2. Spread out your backup locations
It’s better to back up your data in different locations because if one location develops problems or fails, the same data you need will still be available from another location. It may be redundant to create a second backup to your first backup, but you will never know when unforeseen emergencies will happen so it’s better to be safe than sorry.
3. Select a backup solution
Locally, remotely or a combination of the two can be your backup solution. You can use commands and tools that are built in your server management to store files locally. With local backups, you can easily restore those files within a reasonable amount of time. Remote backups have the advantage of restoring your files from a recent restore point and it minimizes data loss. Secure File Transfer Protocol is an example of a good tool for storing remote copies of your data in different locations.
4. Automate the backup process
Manual backing up of your data is a tedious and time-consuming process. It’s better to automate the backup process because it saves you effort and time that you can devote for other important tasks. Ask your VPS service provider if your server hosting control panel has an automatic backup system you can use for managing and setting up backups for your server. In this way, you can configure your server management system to automatically back up your VPS after a specific period of time like daily, weekly or monthly.
5. Test the server backups
After each backup of your data, you should test the backups to make sure they are properly configured. Regularly testing your backups will help determine if the backup configurations are correct and if the system can successfully restore the back-up data. Regular testing will also ensure that the backup solutions you created for your VPS will work as expected and they will not fail you at the last minute when you need them the most.
6. Create a regular backup schedule
Your backup schedule can be done daily, weekly or monthly. Daily backups can be performed at the start or at the end of the day, and they are ideal if you’re using your VPS for a personal account or other types of websites that are always updated with data. You can schedule weekly backups every seven days or four times in a month. Monthly backups are only scheduled once a month and are usually ideal for websites that have static content.
What is a VPS Hosting Service
 A VPS hosting service is the web hosting service offered by a web hosting provider or third-party vendor who will provide the service to paying customers or end-users. The service providers offer VPS hosting plans that you pay for a specific monthly subscription fee with each plan having specific features about RAM, SSD disk space, bandwidth and other specifications that will depend on the amount you pay. If you have decided that VPS is the best web hosting option for you, then you should look around for the best VPS service provider who will meet the specific needs and requirements of your websites and applications.
A VPS hosting service is the web hosting service offered by a web hosting provider or third-party vendor who will provide the service to paying customers or end-users. The service providers offer VPS hosting plans that you pay for a specific monthly subscription fee with each plan having specific features about RAM, SSD disk space, bandwidth and other specifications that will depend on the amount you pay. If you have decided that VPS is the best web hosting option for you, then you should look around for the best VPS service provider who will meet the specific needs and requirements of your websites and applications.
Web hosting service companies are the main vendors or providers of VPS hosting services for individuals and organizations that need virtual private servers to host their websites, applications and other services that need web hosting. Before you choose a VPS hosting service provider, you should first familiarize yourself with VPS hosting especially if you know little about it. The subject areas about VPS services that you should research about are the differences between the main types of web hosting, the specific types of VPS hosting, and the advantages and disadvantages of VPS hosting.
Comparing VPS Hosting to Other Hosting Options
The most common types of web hosting solutions are VPS hosting service, dedicated hosting, cloud hosting and shared hosting. Knowing the differences between these hosting options can help you make an informed decision on what is the best option for your website.
1. Shared Hosting
If your website is still new and still doesn’t have a huge traffic volume, then shared hosting is ideal for you. In this hosting solution, you share a physical server and its resources such as CPU, RAM and hard disk space with other users of the same server. It’s a good hosting model for small business or personal websites and web apps with little traffic, minimum security or performance requirements and few technical needs, and it’s also budget-friendly and cost-effective.
However, since you and other users are sharing resources on the same server and allocated a fixed amount of the server’s capacity, the VPS service provider will not allow any website to scale beyond the limits of a user’s hosting plan. The computing power and memory that you use is affected by the needs of the other subscribers. For example, when a customer on the shared server has a sudden increase of web traffic which will unexpectedly consume more resources, this could cause performance issues for your website or apps.
2. Dedicated Hosting
Under dedicated hosting model, you will rent or pay for a single physical server that is allocated only for you. You have exclusive access and control over the machine, its hardware and resources, and you can install your own OS and other software on it. Dedicated hosting is ideal for large websites that receive an enormous amount of web traffic. Its benefits include hardware flexibility and transparency, workload control and placement, and better security and performance.
However, dedicated hosting costs more than shared and VPS hosting services. If you opt for an unmanaged dedicated server, you should have the experience and skills in server administration and management. You can also choose a dedicated server managed by the VPS service provider, but you will also have to pay extra for this kind of setup.
3. Cloud Hosting
This hosting option consists of a cluster or network of connected physical servers that all work together to provide the disk space, memory, CPU and other resources to the server assigned to a user. Unlike a VPS hosting in which virtual machines located in one physical server are dedicated to individual users, the cloud hosting resources are spread out among a cluster of physical machines located in different data centers.
4. VPS Hosting
VPS hosting is essentially an intermediate between shared hosting and dedicated hosting. A single physical machine is compartmentalized into separate servers with each of them having a dedicated allocation for bandwidth, storage, CPU, RAM and installation of your own OS and software. With a VPS service, you are practically getting the benefits of a dedicated server for an affordable price.
How Much for VPS Hosting
The amount you will pay for VPS hosting services will depend on the needs of your website and on the features of the hosting plan. You can choose a budget-friendly hosting plan or select a pricier plan that contains more configurations and other features. For example, a Windows-based VPS hosting plan will cost more than a Linux-based VPS, which usually costs $10 to $20 less than Windows-based VPS. Depending on the plan configuration, a VPS hosting service plan can go as low as $5 per month to as high as $100 per month
High-Quality, Affordable VPS Services from ServerHub
At ServerHub, you can select from the best VPS service packages that will meet the requirements of your websites and applications and fit your budget. We offer IronGrid Pure SSS plans and IronGrid Bid Data plans that start at just 5$ per month. If you need high-volume VPS plans, we also provide High IOPS SSD plans starting at $45 per month and Enterprise Grade SSD plans starting at $80 per month.
All of our VPS hosting service packages feature instant virtualization deployments, 10Gig network links, comprehensive repositories of operating systems, and scalable resources that can be changed at your request. Contact us to know more about the specific features of our VPS hosting packages and how we can help you choose the best VPS service package that will fit your budget and server requirements.
References & Other Resources:
- What is VPS Hosting?
- What is a VPS? A Beginners Guide to VPS Hosting
- Is There Any Free VPS?
- Overview of Cloud Hosting
- How Does VPS Work?
- What Is a VPS? A Beginner’s Guide to Virtual Private Servers
- Top 10 Benefits of Managed VPS Hosting
- Virtual Private Server definition, advantages, and is it worth it?
- Top 5 reasons to deploy a private cloud
- How Many Daily Visitors Can a VPS Handle?